“Success is not final, failure is not fatal: it is the courage to continue that counts.”
Winston Churchill
The history of e-learning is a colorful one, including stories of teaching robots from the early 1900s and up to awe-inspiring success stories from the 2000s. In this article, we will give you an overview of all the most significant events in the history of e-learning through an interactive timeline.
What is the History of E-Learning?
In 1999, the phrase “E-Learning” was mentioned for the first time in a professional context by Elliott Masie during the TechLearn conference at Disneyworld. However, the very first attempts at e-learning can be traced back to 1924, when Ohio State University professor Sidney Pressey created the very first electronic learning machine, the Automatic Teacher.
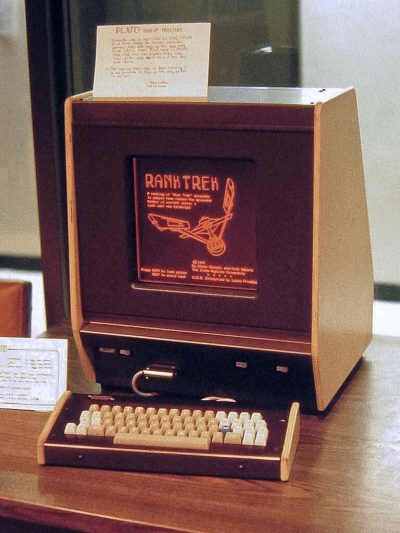
Perhaps the most significant invention in the history of online learning technology is the PLATO. The PLATO is a computer system designed by Donald L. Bitzer in 1960, and it was groundbreaking for its time.
Two decades before the invention of the World Wide Web, the PLATO network could host thousands of users at its peak, and much of the greatest instructional software of the century across many educational disciplines was created on PLATO. The PLATO terminals were very expensive at $5000-$7000 each, but they were worth every penny.

It must be noted, though, that not all inventions in the field of online learning and e-learning were as praised as the PLATO, which went through numerous successful re-releases and four generations. The success stories tend to be highlighted more often than the failures, but it’s just as important to highlight those innovations which failed to reach the masses. The earliest inventions in educational technology may have been clumsy and basic by today’s standards, but they served a crucial role in the development of the history of e-learning.
Timeline of Historical Events in E-Learning
Explore the timeline of all major events related in the history of e-learning and online learning. See how far we have come within a short period of time. The images were retrieved from Wikimedia Commons.
1642: Pascal's Calculator
Blaise Pascal designed the very first mechanical calculator in 1642, when he was only 19 years old. Despite the significance of his invention, he only managed to sell 20 units within a period of 12 years.
1728: First Distance Learning Course
In 1728, Caleb Philips from Boston created the very first distance learning course. The course lessons were delivered to students weekly through regular mail.
1924: The Automatic Teacher
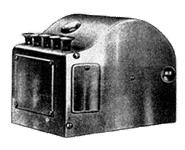
1957: The Teaching Machine
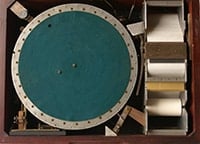
1960: PLATO

Professor Don Bitzer from the University of Illinois created the first computer-based education tool, called the PLATO (Programmed Logic for Automatic Teaching Operations). In the beginning, PLATO was used to deliver computer-based education in order to improve student literacy. However, the device quickly outgrew its strictly educational purpose and became a cornerstone in modern multi-user computing. PLATO is the direct ancestor of modern E-Learning systems such as Blackboard and WebCT.
1966: Computer-managed Instruction
1969: ARPANET
1977: Apple II Personal Computer

In 1977, the Apple II personal computer is released, with Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak highlighting education as the primary intended application for the new hardware. Apple II featured color graphics and sounds, which was highly impressive for the time, and which made the devices particularly appealing to the young demographic.
1979: Apple Partners with Bell & Howell
1983: The Electronic University Network
The Electronic University Network (EUN), an online educational network, is launched by former president of Atari Ron Gordon. It was established to help universities and colleges start utilizing online courses.
1986: A Quarter of High Schools Use PC’s
1989: World Wide Web (WWW)
The World Wide Web (WWW) is invented by British scientist Tim Berners-Lee. The WWW’s original purpose was information-sharing between academic institutions around the world.
1994: First Online School
1999: Term “E-Learning” is First Used
1999: First Online University
2002: MIT’s OpenCourseWare
2008: Term "MOOC" is First Used
2012: The Year of the MOOC
2014: Most Universities Use E-Learning
2018: E-Learning Reaches $168.8 Billion
In 2018, the global E-Learning market size reached $168.8 billion.
2020: Most Corporations Use E-Learning
Approximately 90% of US corporations now use online learning.
What's Next for E-Learning?
Only time will tell in which directions of the evolution of online learning is going to progress from now on. One thing is for sure, though – e-learning isn’t going anywhere. The past history of e-learning has shown that it’s currently on a path of exponential growth, and analysts agree that this growth will only continue to accelerate with time. Time will show whether and which kind of effect this kind of growth will have on traditional learning institutions, but it’s likely that they will need to redesign and adapt themselves to e-learning practices in order to stay competitive in the educational industry.
In the coming years, I believe that the biggest innovations in online learning will make use of adaptive e-learning, which is a type of e-learning that is able to adapt itself and its training materials according to the skillsets and knowledge level of each individual student. Personalized learning is the way of the future, and e-learning is undoubtedly one of the best ways of achieving truly personalized learning outcomes.
The history of e-learning is still in its early stages, and the industry is always looking for new innovators to push the sector further. You do have the chance to be at the forefront of it all – the world is waiting for the next round of innovators in educational technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will answer some of the most commonly asked questions related to the history of e-learning and online learning.
When did online learning start?
What was the first online university?
When was the first online school created?
Who invented e-learning?
In order to answer the question of who invented e-learning, it’s necessary to differentiate offline e-learning and online learning. The first attempts at an offline e-learning device were made by Sidney Pressey, who invented the Automatic Teacher in 1924. However, the first e-learning system which could handle online networking, the PLATO, was invented by Donald Bitzer in 1960.


